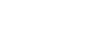Key Highlights
- Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy (CBT) is a highly effective form of therapy for various mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety disorders, and substance abuse.
- CBT focuses on challenging and changing negative thoughts and behaviours to improve emotional regulation and develop coping strategies.
- The origins of CBT can be traced back to the merging of behaviour therapy and cognitive therapy in the 1960s.
- The core techniques of CBT include identifying and challenging negative thoughts, conducting behavioural experiments, and utilizing homework assignments.
- CBT has been proven to be effective in managing conditions such as anxiety, depression, phobias, and obsessive-compulsive disorders.
- Research findings support the effectiveness of CBT, and it is recommended as the first line of treatment for many psychological disorders.
What is CBT?
Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy, also known as CBT, is a form of therapy that has gained significant recognition and popularity in the field of mental health. It is widely regarded as one of the most effective treatment approaches for various mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety disorders, and substance abuse. This blog will provide an in-depth understanding of Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy, its origins, key principles, including the role of psychological issues, core techniques, and its effectiveness in treating mental health problems.
CBT is a form of psychotherapy that focuses on challenging and changing negative thoughts, beliefs, and attitudes, as well as associated behaviours. The goal of CBT is to improve emotional regulation and develop personal coping strategies that target solving current problems. What sets CBT apart from other therapeutic approaches is its problem-focused and action-oriented nature. Instead of delving into the unconscious meaning behind behaviours, CBT focuses on practical strategies to address specific problems related to diagnosed mental disorders. The therapist’s role is to assist the client in finding and practicing effective strategies, such as cognitive behaviour therapy, to alleviate symptoms and achieve their treatment goals by reframing negative thoughts into positive feelings and behaviors. This type of therapy is highly effective and has been proven to help individuals overcome a wide range of mental health issues.
Understanding Cognitive-Behavioural Psychotherapy
Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy, also known as CBT, is a form of therapy that aims to reduce symptoms of various mental health conditions. It is primarily used to treat depression and anxiety disorders, but its applications have expanded to include many other issues and mental health conditions, such as substance use disorders, marital problems, ADHD, and eating disorders. This type of therapy, also known as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), is a structured and goal-oriented form of talk therapy that can help manage both psychological and non-psychological health conditions, including medical conditions, making it a highly versatile and effective form of cognitive behavioural therapy.
CBT is based on the belief that thought distortions and maladaptive behaviours play a role in the development and maintenance of many psychological disorders. It focuses on challenging and changing cognitive distortions, which are negative thoughts, beliefs, and attitudes, as well as their associated behaviors. By addressing these distortions, individuals can improve their emotional regulation and develop personal coping strategies to solve current problems.
Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy is a form of talk therapy that combines principles from behavioural and cognitive psychology. It differs from historical approaches to psychotherapy, such as the psychoanalytic approach, by focusing on specific problems related to diagnosed mental disorders. The therapist’s role is to assist the client in finding and practicing effective strategies to address their identified goals and alleviate symptoms of the disorder.
CBT includes a number of cognitive or behavioural psychotherapies that treat defined psychopathologies using evidence-based techniques and strategies. It is a collaborative and goal-oriented approach that involves active participation from both the therapist and the client. The therapist helps the client identify and challenge negative thoughts and behaviors while the client actively engages in homework assignments and practice outside of therapy sessions.
The Origins and Evolution of Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy
The origins of Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy can be traced back to the merging of behaviour therapy and cognitive therapy in the 1960s. Behaviour therapy, which focuses on observable behaviours and their environmental determinants, and cognitive therapy, which focuses on thoughts and beliefs as determinants of behaviour, were combined to create a more comprehensive and integrated approach to therapy.
One of the pioneers of Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy is Aaron T. Beck, who developed cognitive therapy in the 1960s. Beck proposed that individuals’ negative thoughts and beliefs contribute to the development and maintenance of psychological disorders. By challenging and changing these negative thoughts and beliefs, individuals can alleviate their symptoms and improve their emotional well-being.
Another influential figure in the development of Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy is Albert Ellis, who developed rational emotive behavior therapy (REBT) in the 1950s. REBT focuses on identifying and challenging irrational beliefs that contribute to emotional distress. Through the process of disputing irrational beliefs, individuals can develop more rational and adaptive thoughts and behaviors.
Over the years, Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy has evolved and expanded to include various techniques and strategies. It has been adapted for different populations and specific disorders, making it a versatile and effective treatment approach for a wide range of mental health conditions.
Key Principles Behind Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy
The key principles behind Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy (CBT) revolve around the understanding that negative thoughts, beliefs, and attitudes play a significant role in the development and maintenance of psychological disorders. CBT focuses on challenging and changing these cognitive distortions and their associated behaviors, also known as behavior patterns, to improve emotional regulation and develop personal coping strategies. One type of CBT, dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), specifically addresses destructive or disturbing thoughts and behaviors while incorporating treatment strategies such as emotional regulation and mindfulness. By identifying and replacing negative thoughts with positive thoughts, individuals can break the cycle of negative thinking and improve their overall well-being.
The principles of CBT are rooted in the belief that thoughts, feelings, and behaviours are interconnected and influence each other. Negative thoughts and beliefs can lead to negative emotions and maladaptive behaviours, perpetuating a cycle of distress and dysfunction. By identifying and challenging these negative thoughts and beliefs, individuals can break free from this cycle and develop more positive and adaptive ways of thinking and behaving.
Another key principle of CBT is the emphasis on the present moment and the here and now. CBT is a problem-focused and action-oriented form of therapy, meaning it is used to address specific problems related to a diagnosed mental disorder. The focus is on finding practical strategies and solutions to alleviate symptoms and improve the client’s overall well-being.
Additionally, CBT recognizes the importance of the therapeutic relationship between the therapist and the client. The therapist serves as a guide and collaborator, working together with the client to identify goals, develop strategies, and monitor progress. The therapeutic relationship is built on trust, empathy, and mutual respect, creating a safe space for the client to explore and challenge their thoughts and behaviours.

Core Techniques of Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy
The core techniques of Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy (CBT) involve identifying and challenging negative thoughts and behaviours, as well as developing new coping strategies. CBT is a collaborative and goal-oriented approach that encourages active participation from the client.
Some of the core techniques of CBT include cognitive restructuring, which involves identifying and challenging negative thoughts and replacing them with more positive and realistic ones. Behavioural experiments and exposure therapy are also used to help clients confront and overcome their fears and anxieties. Homework assignments play a crucial role in CBT, as they provide opportunities for clients to practice and apply new coping strategies outside of therapy sessions. These techniques may involve some risks, such as temporary stress or anxiety, but working with a skilled therapist will minimize any negative feelings and the coping skills you learn can help you manage and conquer them.
Identifying and Challenging Negative Thoughts
One of the key techniques in Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy is identifying and challenging negative thoughts. Negative thoughts, also known as cognitive distortions, can contribute to the development and maintenance of various mental health conditions. Common cognitive distortions include black-and-white thinking, overgeneralization, and catastrophizing. In CBT, individuals learn to recognize and challenge these distortions by examining the evidence for and against their thoughts, considering alternative perspectives, and reframing negative thoughts with more realistic and balanced ones. This technique helps individuals to improve their emotional well-being and develop more adaptive coping strategies.
Behavioural Experiments and Exposure Therapy
In addition to challenging negative thoughts, Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy incorporates behavioural experiments and exposure therapy. Behavioural experiments involve testing out beliefs or assumptions through real-life experiences. For example, a person with social anxiety may conduct a behavioural experiment by attending a social event and observing their actual level of discomfort or the reactions of others. This helps to challenge and modify maladaptive beliefs or fears. Exposure therapy, on the other hand, involves gradually and systematically exposing individuals to situations or stimuli that trigger anxiety or fear. This type of therapy, known as stress inoculation training, helps individuals to confront and overcome their anxieties, leading to a reduction in symptoms over time.
The Role of Homework in Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy
Homework assignments play an important role in Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy as they help individuals apply the skills and strategies learned in therapy sessions to their daily lives. These assignments can include keeping thought records, practicing relaxation techniques, or engaging in behavioural experiments. Homework assignments provide an opportunity for individuals to practice new skills, reinforce learning, and track progress. By completing homework, individuals can maximize the benefits of therapy sessions and continue their progress outside of the therapeutic setting.

Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy for Various Conditions
Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy (CBT) is a versatile treatment approach that can be applied to a wide range of mental health conditions. It has been proven effective in managing anxiety and depression, addressing phobias and obsessive-compulsive disorders, and improving behavioural disorders and anger management.
Managing Anxiety and Depression
CBT has been extensively studied and proven effective in managing anxiety and depression. By helping individuals identify and challenge negative thoughts and behaviours, CBT can reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression and improve overall mental health. CBT teaches individuals skills to manage symptoms, develop healthier coping strategies, and improve their emotional well-being. It is recommended as a first-line treatment for anxiety and depression, particularly in children and adolescents.
Addressing Phobias and Obsessive-Compulsive Disorders
CBT is also highly effective in addressing phobias and obsessive-compulsive disorders (OCD). Intense and irrational fears of specific objects or situations characterize phobias, while OCD is characterized by intrusive thoughts and compulsive behaviors. CBT helps individuals confront and overcome their fears through exposure therapy and behavioral experiments, making it a recommended treatment for both phobias and obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD). By gradually facing their fears and resisting compulsive behaviors, individuals with these disorders can experience significant symptom reduction and improved quality of life.
Improving Behavioral Disorders and Anger Management
Behavioural disorders and anger management issues can significantly impact an individual’s daily life and relationships. CBT provides effective strategies for improving behavioural disorders and anger management. By identifying and challenging negative thought patterns and developing coping skills, individuals can learn healthier ways to manage their behaviour and emotions. CBT helps individuals gain insight into the underlying causes of their behavioural issues and provides practical tools to address them. Through CBT, individuals can develop healthier behaviours, improve self-control, and enhance their overall well-being.
The Effectiveness of Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy
Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy (CBT) has been extensively researched and proven to be a highly effective way of treating a wide range of mental health disorders. It is recommended as a first-line treatment for many psychological conditions, particularly anxiety and depression. Research findings have shown that CBT is as effective as medication for treating less severe forms of depression, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), substance use disorders, eating disorders, bipolar disorder, and borderline personality disorder. CBT has also been found to be particularly effective when combined with medication for the treatment of major depressive disorder.
Research Findings on Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy Outcomes
Numerous research studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy (CBT) in improving mental health outcomes. For example, studies have shown that CBT is effective in reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression, improving emotion regulation, and enhancing overall well-being. CBT has also been found to be effective in treating specific conditions such as phobias, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and behavioural disorders. Research findings consistently support the use of CBT as an evidence-based treatment approach for various mental health conditions, including chronic fatigue syndrome, with the United Kingdom’s National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommending CBT in treatment plans for a number of mental health difficulties.
Comparative Analysis with Other Therapeutic Approaches
Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy (CBT) has shown equal or greater effectiveness in treating many mental health conditions. For example, research studies have found that CBT is as effective as other psychotherapies for the treatment of depression and anxiety disorders. CBT has also been found to be more effective than other interventions, such as supportive therapy or waitlist control conditions. However, the choice of therapy should be based on individual needs and preferences, and some individuals may benefit more from a different therapeutic approach, highlighting the importance of understanding the different types of therapy available.
Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy Techniques in Practice
Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy (CBT) utilizes various techniques to help individuals challenge and change negative thoughts, develop coping strategies, and improve emotional regulation. Some of the key techniques used in CBT include cognitive restructuring, relaxation techniques, and the use of case studies and success stories.
A Closer Look at Cognitive Restructuring
Cognitive restructuring is a core technique in Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy (CBT) that involves identifying and challenging negative thoughts and replacing them with more positive and realistic ones. By examining the evidence for and against negative thoughts, individuals can gain a more balanced perspective and reduce distressing emotions. Cognitive restructuring helps individuals develop more adaptive thoughts and beliefs, leading to improved emotional well-being and the development of healthier coping strategies.
The Importance of Relaxation Techniques and Mindfulness
Relaxation techniques and mindfulness are important components of Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy (CBT). These techniques help individuals manage stress, reduce anxiety, and improve overall well-being. Relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing and progressive muscle relaxation, promote physical and mental relaxation. Mindfulness, on the other hand, involves being fully present and aware of the present moment without judgment. By incorporating relaxation techniques and mindfulness into daily life, individuals can enhance their ability to cope with stress and improve their emotional health.
Case Studies: Success Stories of Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy
Case studies and success stories are valuable tools in Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy (CBT) as they provide real-life examples of individuals who have benefited from the therapy. These case studies help individuals understand how CBT techniques are applied in practice and the positive outcomes that can be achieved. By highlighting success stories, individuals can gain hope and motivation to engage in CBT and work towards their own healing and personal growth.
Preparing for Your First Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy Session
Preparing for your first Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy (CBT) session can help set the stage for a successful therapeutic journey. Feeling uncertain or anxious about the first appointment is normal, but being prepared and knowing what to expect can help ease any concerns. The initial consultation and subsequent therapy sessions are important steps in the healing process, and being proactive in preparing for them can maximize the benefits of therapy.

What to Expect During the Initial Consultation
The initial consultation is the first step in Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy (CBT) and serves as an opportunity for the therapist to assess your needs, goals, and concerns, specifically for young people. During the first session, also known as the initial consultation, the therapist will gather information about your mental health history, current symptoms, and any relevant life experiences. They will also discuss the therapy process and confidentiality and answer any questions you may have, including how goal setting can be incorporated into your treatment plan. It is important to be open and honest during this session, as it will help the therapist tailor the treatment to your specific needs.
How to Maximize the Benefits of Your Therapy Sessions
To maximize the benefits of your Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy (CBT) sessions, it is important to actively engage in the therapeutic process and apply the skills and strategies learned in therapy to your daily life. This involves completing homework assignments, practicing the techniques in therapy, and regularly attending therapy sessions. It is also important to talk openly share any concerns or challenges you may be facing with your therapist, and actively participate in the treatment planning process. By actively engaging in therapy, you can enhance the effectiveness of CBT and experience positive changes in your mental health.
How does cognitive behavioral psychotherapy differ from other types of therapy?
Cognitive behavioral psychotherapy focuses on changing negative thought patterns and behaviors to address psychological issues. Unlike traditional psychotherapy that explores past experiences, CBT is present-focused, goal-oriented, and emphasizes practical strategies to help individuals overcome challenges.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cognitive behavioural psychotherapy offers a structured approach to addressing various mental health conditions through techniques like cognitive restructuring and relaxation practices. Its proven effectiveness, supported by research findings and success stories, emphasizes its significance in therapy. Whether managing anxiety, phobias, or behavioural disorders, cognitive behavioural psychotherapy provides a path to healing and growth. Preparation for therapy sessions and understanding what to expect can enhance the benefits of this therapeutic approach. If you’re considering cognitive behavioural psychotherapy, seek a qualified therapist and embark on a journey toward improved mental well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Does Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy Typically Last?
Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy (CBT) is a time-limited treatment approach that typically lasts for a specific number of sessions. The duration of CBT can vary depending on the individual’s specific needs, goals, and progress. In general, CBT is a short-term treatment that can range from a few weeks to several months. The length of therapy may also be influenced by the complexity of the individual’s presenting issues and the severity of their symptoms. It is important to discuss the expected duration of CBT with your therapist, as they can provide a more accurate estimate based on your specific circumstances.
Can Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy Be Conducted Online?
Yes, Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapy (CBT) can be conducted online through computerized or internet-delivered programs. Online CBT, also known as internet-delivered CBT or ICBT, has been shown to be effective in treating various mental health conditions, including anxiety and depression. Online CBT provides a convenient and accessible way for individuals to receive therapy, particularly for those who may have barriers to accessing traditional face-to-face therapy. Online CBT programs often include interactive modules, therapeutic exercises, and support from trained professionals.
How to Find a Qualified Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapist?
Finding a qualified Cognitive Behavioral Psychotherapist involves conducting research, seeking referrals, and considering factors such as the therapist’s qualifications, experience, and specialization. A good starting point is to consult with your primary care physician or mental health professional for recommendations. It can also be helpful to search online directories or professional organizations that specialize in connecting individuals with qualified therapists. When selecting a therapist, consider factors such as their credentials, experience with the specific mental health condition you are seeking help for, and their approach to therapy. It is also important to schedule an initial consultation to ensure a good fit between you and the therapist.